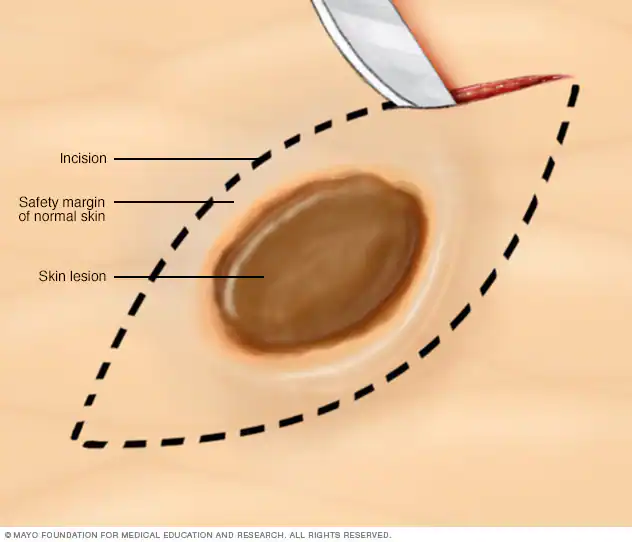
Excision
Skin excision is the most effective treatment of skin cancers including Melanomas, BCCs and SCCs.
The art of skilled surgeons is to offer results that are both medically and cosmetically acceptable. Excision has a high cure rate and allows for microscopic examination of surrounding tissue.
While wide local excision is a safe and effective procedure, all medical procedures carry some risk, though they are minimized in the hands of a qualified doctor. Risks include: infection, scarring, bleeding, allergic reaction to anaesthetic, and healing problems.
In wide-local excision, skin cancer and a margin of healthy skin around it is cut out, usually in the shape of an ellipse. The ellipse is often designed so that the resulting scar runs parallel with existing skin creases. This usually provides a wound under less tension and orientates the scar in a direction which is less noticeable to the eye. Scars are usually 3 – 4 times longer than the original lesion. The tissue is then sent for processing and margin evaluation by a pathologist. Once the tissue has been removed, the edges of the wound are sutured together. There are usually two layers of sutures (stitches) a layer underneath that is absorbable and a layer of sutures on the surface which will need to be removed in 5 – 14 days.